3D Graphics Programming with QuickDraw 3D 1.5.4
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |
Ellipsoids
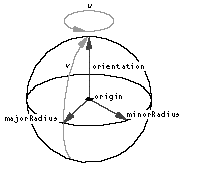
Figure 16 shows an ellipsoid.
Data Format
Vector3D orientation
Vector3D majorRadius
Vector3D minorRadius
Point3D origin
Float32 uMin
Float32 uMax
Float32 vMin
Float32 vMax
- orientation
- The orientation of the ellipsoid.
- majorRadius
- The major radius of the ellipsoid.
- minorRadius
- The minor radius of the ellipsoid.
- origin
- The origin (that is, the center) of the ellipsoid.
- uMin
- Minimum parametric limit value for u. To understand u, first consider u for the ellipse determined by majorRadius and minorRadius .The value of u on this sub-ellipse is parametrized by the angle between the major axis and the vector from the origin to the circumference of the ellipse. The value u = 0 corresponds to 0 radians, and u = 1 corresponds to 2 radians.The values uMin and uMax are used to create partial ellipses. The basic idea is that only the part of the ellipse between uMin and uMax is drawn. For such a particular partial sub-ellipse, the partial ellipsoid can be thought of as the result of keeping uMin and uMax fixed but letting v vary through its admissible range. For details, see the QD3D documentation or develop magazine, Dec. 96. Must be 0 in Version 1.5.
- uMax
- Maximum parametric limit value in u direction; see uMin above. Must be 1 in Version 1.5.
- vMin
- Minimum parametric limit value for v. To understand v, first consider v for the ellipse determined by majorRadius and orientation. The value of v on this sub-ellipse is parametrized by the angle between the major axis and the vector from the origin to the circumference of the ellipse. The value v = 0 corresponds to 0 radians, and v = 1 corresponds to (not 2) radians. The values vMin and vMax are used to create partial ellipses of this sub-ellipse. The basic idea is that only the part of the ellipse between vMin and vMax is drawn. Let pMin be the endpoint of the partial sub-ellipse that corresponds to vMin , and pMax be the endpoint that corresponds to vMax . Then the partial ellipsoid is the result of truncating the whole ellipsoid by a two planes parallel to the plane specified by majorAxis and minorAxis : one of these planes passes through vMin and the other plane passes through vMax . For details, see the QD3D documentation or develop magazine, Dec. 96. Must be 0 in Version 1.5
- vMax
- Maximum parametric limit value in v direction; see vMin above. Must be 1 in Version 1.5.
Description
An ellipsoid is a three-dimensional object defined by an origin (that is, the center of the ellipsoid) and three pairwise orthogonal vectors that define the orientation and the major and minor radii of the ellipsoid.
Default Surface Parameterization
The default surface parameterization for an ellipsoid is as shown in Figure 16 . To the left of the major radius, v = 0; to the right of the major radius, v = 1. At the (top of the) orientation vector, and at the bottom of the ellipsoid, u = 0.
Example
Ellipsoid ( )
Ellipsoid (
2 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
0 0 0
0 # uMin
1 # uMax
0 # vMin
1 # vMax
)
Container (
Ellipsoid ( )
Container (
AttributeSet ( )
DiffuseColor ( 1 1 0 )
)
)
© 1997 Apple Computer, Inc.
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |